Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are two distinct types of arthritis with different causes, characteristics, and treatment approaches. IRIS Hospital in Thiruvananthapuram is a Rheumatology Speciality Centre offering diagnosis & treatment for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes, Symptoms & Treatment: Osteoarthritis Vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
Causes:
OA is primarily caused by the wear and tear of joint cartilage over time. It is often associated with aging, joint injury, obesity, and overuse of joints.
RA is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, primarily the synovium (the lining of the joints). The exact cause of RA is not fully understood, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of OA typically include joint pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. These symptoms tend to worsen over time and are often worse after periods of activity or inactivity.
Symptoms of RA include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and warmth, which may be symmetrical (occurring on both sides of the body). RA symptoms are usually more severe in the morning or after periods of rest and may improve with movement.
Joint Involvement:
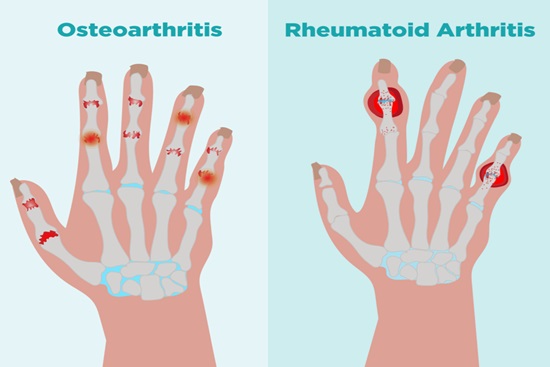
OA commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, as well as the hands and fingers.
RA typically affects multiple joints, including small joints in the hands and feet, as well as larger joints such as the knees, wrists, and elbows. It tends to be symmetrical, affecting the same joints on both sides of the body.

Inflammatory Response:
While inflammation may be present in OA, it is not typically a primary feature of the condition. Inflammation in OA is usually localized to the affected joint and is milder compared to RA.
RA is characterized by significant inflammation in the synovium, leading to joint swelling, redness, and warmth. Systemic inflammation can also affect other organs and tissues in the body.
Treatment:
OA treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving joint function. This may include medications for pain relief (e.g., acetaminophen, NSAIDs), physical therapy, exercise, weight management, and assistive devices.
RA treatment aims to suppress inflammation, reduce symptoms, and prevent joint damage. This typically involves a combination of medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic agents, corticosteroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Physical therapy and lifestyle modifications may also be recommended.
