Degenerative joint diseases, also known as degenerative joint disorders or osteoarthritis (OA), involve the gradual deterioration of the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones within the joints. These diseases are characterized by progressive damage to joint tissues, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Types of Degenerative Joint Diseases:
Osteoarthritis (OA)
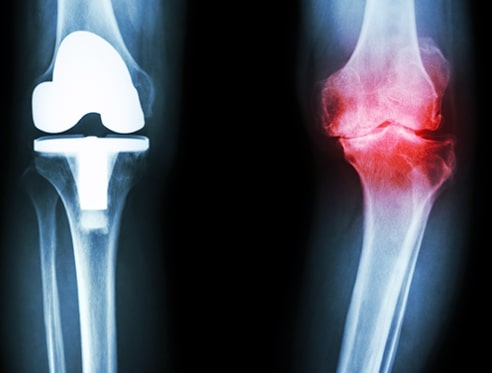
OA is the most common form of degenerative joint disease. It occurs when the protective cartilage that covers the ends of bones wears down over time, resulting in bone-on-bone contact, inflammation, and the formation of bone spurs. OA can affect any joint but most commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, spine, and hands.
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
DDD is a condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the spine. As these discs degenerate and lose their elasticity, they can become less effective at cushioning the vertebrae, leading to back pain, stiffness, and reduced spinal flexibility. DDD is a common cause of chronic low back pain in older adults.
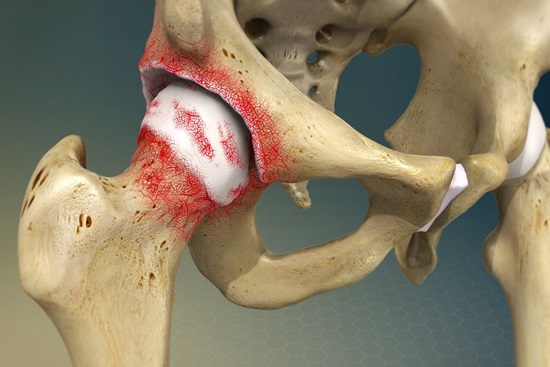
Degenerative Joint Disease of the Hip
This refers to the progressive deterioration of the hip joint, typically due to osteoarthritis. It can lead to hip pain, stiffness, and difficulty walking or performing daily activities.
Degenerative Joint Disease of the Knee
Similar to hip degenerative joint disease, knee degenerative joint disease primarily involves the breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, resulting in pain, swelling, and instability.
Degenerative Joint Disease of the Hand
Osteoarthritis can affect the joints of the hands and fingers, leading to pain, swelling, and decreased grip strength. Bony enlargements, known as Heberden's nodes and Bouchard's nodes, may develop on the finger joints.
Degenerative joint diseases often result from a combination of factors, including aging, genetics, joint injury or trauma, repetitive stress on the joints, and obesity. While these conditions are typically chronic and progressive, treatment can help manage symptoms and improve joint function. Treatment options may include medications for pain relief and inflammation, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications (such as weight management and exercise), assistive devices (such as braces or orthotics), and in severe cases, surgery (such as joint replacement). Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential for minimizing pain and disability associated with degenerative joint diseases.
